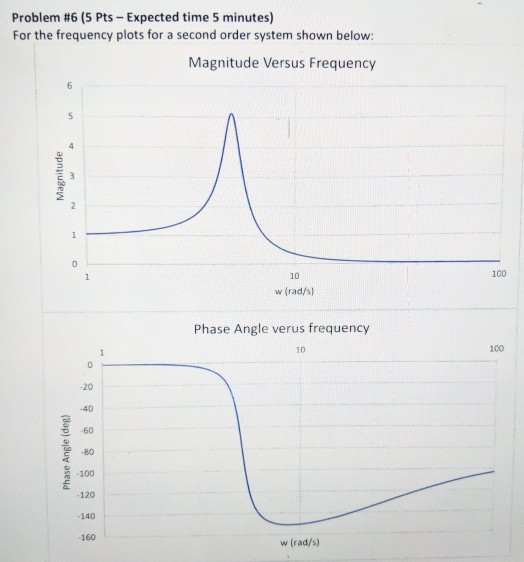
-->
Returns or sets the plot order for the selected series within the chart group. Read/write Long.
Syntax
expression.PlotOrder
All plots follow a logical organization with a beginning, middle, and end—but there's a lot more to the basic plot structure than just this. Generally speaking, every plot has these five elements in this order: Exposition/introduction; Rising action; Climax/turning point; Falling action; Resolution/denouement #1: Exposition/Introduction. I had 5 plots that I needed to reorder. When unsure about the order, permute plots two at a time, refresh the legend and see if that is the order you wanted. The plot structure, also called the dramatic structure, of a story, novel or script includes the events that make up the idea of the writing. These are often laid out as a series of beginning, middle and end details and include five basic elements as well as a conflict.
expression A variable that represents a Series object.
Remarks
You can set plot order only within a chart group (you cannot set the plot order for the entire chart if you have more than one chart type). A chart group is a collection of series with the same chart type.
Changing the plot order of one series will cause the plot orders of the other series in the chart group to be adjusted, as necessary.
Example
This example makes series two on Chart1 appear third in the plot order. The example should be run on a 2D column chart that contains three or more series.
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
What is the Plot of a Story?
If you are currently wondering, 'WHAT IS A PLOT OF A STORY?' we've got the answer!
Last updated on June 28, 2019.
5 Plots In Order Worksheets
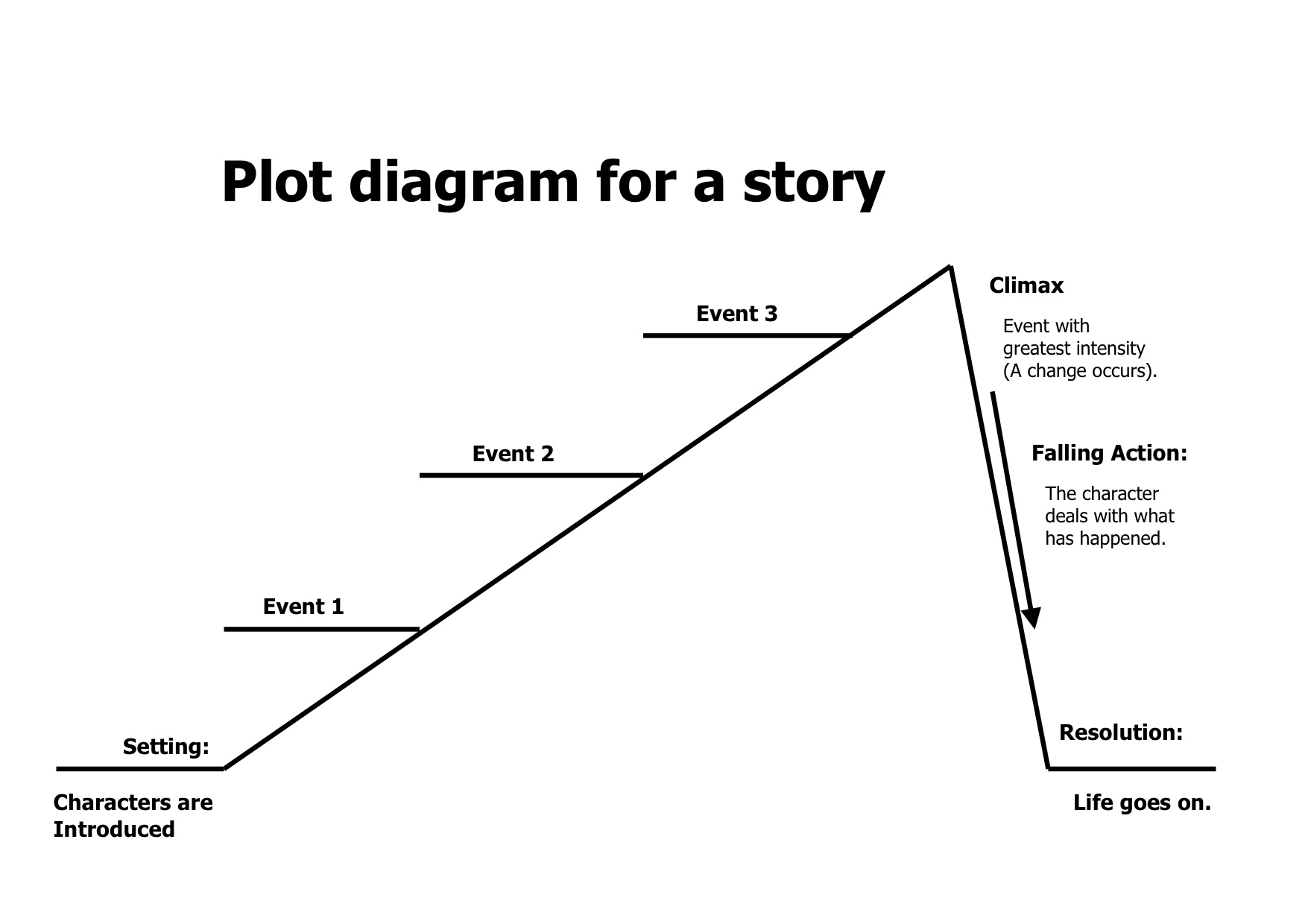
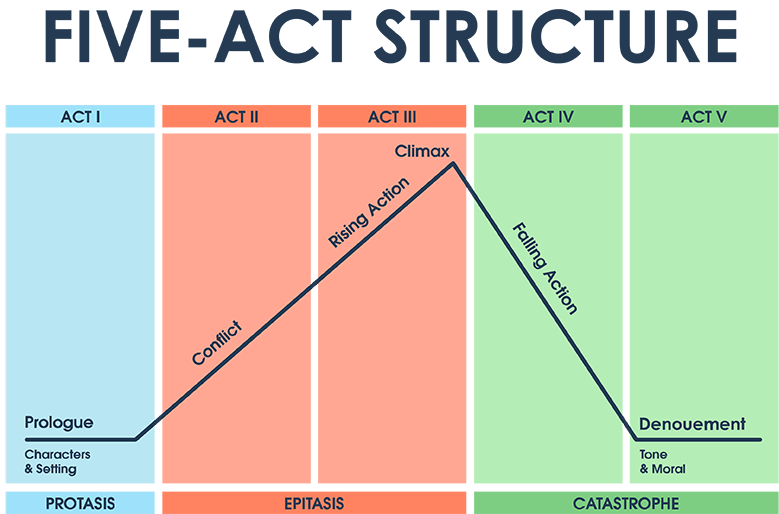
Plot as a literary term is defined as the structure of events that make up the movements of a story through time; characters and settings are organized in a logical pattern of cause-and-effect. A plot can be simple or complex in structure. A complex plot with many interrelated elements is sometimes called an imbroglio. Plot is also sometimes referred to as a storyline.
Five essential elements of plot explained:
1. Exposition/Introduction: In the exposition stage of the plot of a story, the setting and characters (especially the main character, known as the protagonist) are introduced, as well as the main problem, conflict or goal of the story.
2. Rising Action: The rising action stage involves an inciting incident. The inciting incident pushes the plot into motion, events begin to build, the protagonist takes action, and the storyline becomes more complex. During this phase, there is often a sense of tension.
Remarks
You can set plot order only within a chart group (you cannot set the plot order for the entire chart if you have more than one chart type). A chart group is a collection of series with the same chart type.
Changing the plot order of one series will cause the plot orders of the other series in the chart group to be adjusted, as necessary.
Example
This example makes series two on Chart1 appear third in the plot order. The example should be run on a 2D column chart that contains three or more series.
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
What is the Plot of a Story?
If you are currently wondering, 'WHAT IS A PLOT OF A STORY?' we've got the answer!
Last updated on June 28, 2019.
5 Plots In Order Worksheets
Plot as a literary term is defined as the structure of events that make up the movements of a story through time; characters and settings are organized in a logical pattern of cause-and-effect. A plot can be simple or complex in structure. A complex plot with many interrelated elements is sometimes called an imbroglio. Plot is also sometimes referred to as a storyline.
Five essential elements of plot explained:
1. Exposition/Introduction: In the exposition stage of the plot of a story, the setting and characters (especially the main character, known as the protagonist) are introduced, as well as the main problem, conflict or goal of the story.
2. Rising Action: The rising action stage involves an inciting incident. The inciting incident pushes the plot into motion, events begin to build, the protagonist takes action, and the storyline becomes more complex. During this phase, there is often a sense of tension.
3. Climax: The climax is the turning point in the plot of a story. It involves a 'climax' (hence the name) – the central struggle. The protagonist faces the main challenge which will eventually lead to the outcome or goal of the story. Typically, this is the most emotional part of the storyline and it often involves the most action.
4. Falling Action: During this stage, the action winds down, loose ends get tied up, events are resolved and we learn the results of the protagonists' actions.
5. Denoument/Conclusion: In the denoument stage, the goal is resolved and the conflict ends (could be positive, negative or neutral). This is the end of the story.
Without plot, there is no story.
In a story, something has to happen; otherwise, it's not a story. The plot of a story includes the events of the story and conveys the key themes, messages, and meaning of the narrative. It's what gives a story its energy and emotion. A good plot engages readers so they want to know what will happen next.
5 Plots In Order
Did you like this article? Then you might also like '8 Essential Elements of a Story Explained' which covers Setting, Character, Story Plot, Conflict, Theme, Point-of-View, Tone, and Style. Or, check out this perfectly printable PDF of the 8 elements of a story. You might also like 10 Steps to an A+ Essay.

